California's Franchise Tax Board (FTB) plays a crucial role in managing state taxes and ensuring fiscal responsibility for individuals and businesses. If you're a resident of California or operate a business within the state, understanding the FTB's functions and responsibilities is essential. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the FTB, its purpose, and how it impacts your financial obligations.
The FTB is one of the key agencies responsible for tax administration in California. Its primary mission is to collect state taxes efficiently and ensure compliance with tax laws. Whether you're filing personal income taxes or managing corporate taxes, the FTB is the entity you'll interact with most frequently.
As we delve deeper into this topic, you'll gain insights into the FTB's structure, services, and how it affects taxpayers. Whether you're an individual taxpayer or a business owner, having a clear understanding of the FTB can help you navigate the complexities of California's tax system with confidence.
Read also:Trimet A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Its Uses Benefits And Applications
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the California FTB
- Role of the FTB in Tax Administration
- Understanding the Tax Filing Process
- Types of Taxes Managed by the FTB
- FTB Services for Taxpayers
- Ensuring Compliance with FTB Regulations
- Penalties for Non-Compliance
- Resources for Taxpayers
- Frequently Asked Questions About the FTB
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to the California FTB
The Franchise Tax Board (FTB) of California is a government agency responsible for administering state tax laws. Established to ensure the fair collection of taxes, the FTB oversees various types of taxes, including personal income tax, corporate taxes, and more. Its mission is to maintain a balanced tax system that supports California's economic growth while protecting taxpayer rights.
For individuals, the FTB provides guidance on filing income tax returns, managing deductions, and ensuring compliance with state regulations. Businesses, on the other hand, rely on the FTB for information regarding franchise taxes, payroll taxes, and other financial obligations. Understanding the FTB's role is vital for anyone who resides or operates in California.
History of the FTB
The FTB was created in 1935 as part of California's efforts to streamline tax administration. Over the decades, the agency has evolved to address the changing needs of taxpayers and the state's economy. Today, the FTB employs advanced technology and data-driven strategies to enhance its services and improve taxpayer experience.
Role of the FTB in Tax Administration
The FTB's primary responsibility is to administer and enforce California's tax laws. This includes collecting taxes, providing taxpayer assistance, and ensuring compliance. The agency works closely with other state departments to create a cohesive tax system that benefits both the government and its citizens.
One of the key functions of the FTB is to calculate and collect franchise taxes, which are levied on businesses operating in California. These taxes are used to fund essential public services, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. By maintaining transparency and accountability, the FTB strives to build trust with taxpayers.
Key Responsibilities of the FTB
- Administering personal and corporate income taxes
- Enforcing tax laws and regulations
- Providing resources and support for taxpayers
- Conducting audits to ensure compliance
Understanding the Tax Filing Process
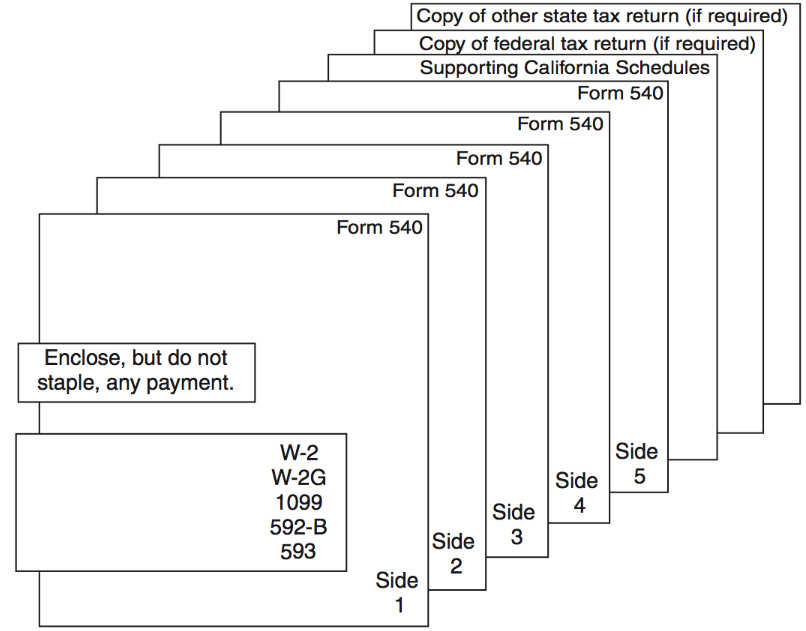
Filing taxes with the FTB involves several steps, each designed to ensure accuracy and compliance. Individuals and businesses must submit their tax returns by the designated deadline, which is typically April 15th each year. The FTB offers both online and paper-based filing options to accommodate different taxpayer needs.
Read also:Go Kickball The Ultimate Guide To A Fun And Competitive Sport
For those who prefer digital solutions, the FTB's online portal provides a user-friendly interface for submitting tax forms, making payments, and tracking the status of returns. Additionally, the agency offers a mobile app, which allows taxpayers to access their accounts and manage their tax obligations on the go.
Steps to File Taxes with the FTB
- Gather all necessary documents, such as W-2s, 1099s, and financial statements
- Complete the appropriate tax forms based on your filing status
- Submit your return through the FTB's online portal or via mail
- Monitor your account for updates and notifications
Types of Taxes Managed by the FTB
The FTB manages a variety of taxes, each tailored to specific groups of taxpayers. These include personal income tax, corporate franchise tax, and other specialized taxes. Understanding the types of taxes you may be subject to is crucial for accurate reporting and compliance.
Personal income tax is the most common tax levied by the FTB and applies to individuals earning income in California. Corporate franchise tax, on the other hand, is assessed on businesses operating within the state. Both taxes are calculated based on income levels and are subject to various deductions and credits.
Specialized Taxes Administered by the FTB
- Non-resident taxes for individuals working in California
- Partnership and S-Corporation taxes
- Withholding taxes for employers
FTB Services for Taxpayers
The FTB offers a wide range of services to assist taxpayers in fulfilling their obligations. These services include online tools, customer support, and educational resources. By leveraging these tools, taxpayers can simplify the tax filing process and reduce the likelihood of errors.
One of the most valuable services provided by the FTB is its online account management system. This system allows taxpayers to view their tax history, make payments, and update their personal information. Additionally, the FTB's customer service team is available to answer questions and resolve issues related to tax filings.
Online Tools and Resources
- FTB e-Services for secure account management
- Taxpayer assistance centers for in-person support
- Webinars and workshops on tax-related topics
Ensuring Compliance with FTB Regulations
Compliance with FTB regulations is essential for avoiding penalties and maintaining financial stability. Taxpayers are encouraged to familiarize themselves with the latest tax laws and guidelines to ensure accurate reporting. The FTB provides regular updates and notifications to help taxpayers stay informed.
In addition to staying informed, taxpayers can take proactive steps to ensure compliance. This includes maintaining accurate records, consulting with tax professionals, and utilizing the FTB's resources for guidance. By prioritizing compliance, individuals and businesses can avoid unnecessary complications and legal issues.
Tips for Maintaining Compliance
- Keep detailed records of income and expenses
- Consult with a tax professional for complex issues
- Utilize the FTB's educational resources and tools
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with FTB regulations can result in significant penalties, including fines, interest charges, and legal action. These penalties are designed to encourage timely and accurate tax filings while deterring fraudulent behavior. Taxpayers who fail to meet their obligations may face severe consequences, making compliance a top priority.
The FTB assesses penalties based on the severity of the violation and the taxpayer's history of compliance. For example, late filings may incur a penalty of 5% of the unpaid tax for each month the return is overdue, up to a maximum of 25%. In cases of intentional non-compliance, penalties can be even more severe.
Common Penalties Imposed by the FTB
- Failure to file penalty
- Underpayment penalty
- Penalty for inaccurate reporting
Resources for Taxpayers
The FTB provides numerous resources to assist taxpayers in understanding and fulfilling their obligations. These resources include publications, videos, and interactive tools designed to simplify the tax filing process. By leveraging these resources, taxpayers can gain a deeper understanding of California's tax system and improve their financial literacy.
For those seeking additional guidance, the FTB offers a directory of certified tax professionals and advisors. These experts can provide personalized advice and support to help taxpayers navigate complex tax issues. Additionally, the FTB's website features a comprehensive FAQ section that addresses common questions and concerns.
Useful Resources from the FTB
- Publications and guides on tax topics
- Video tutorials for online filing
- Contact information for taxpayer assistance centers
Frequently Asked Questions About the FTB
Many taxpayers have questions about the FTB's role and responsibilities. Below are some of the most frequently asked questions, along with detailed answers to help clarify common concerns.
FAQ: What is the FTB's mission?
The FTB's mission is to administer California's tax laws fairly and efficiently, ensuring compliance while protecting taxpayer rights. Through innovative solutions and dedicated service, the FTB aims to build trust and confidence in the state's tax system.
FAQ: How do I file my taxes with the FTB?
You can file your taxes with the FTB using their online portal or by submitting paper forms via mail. Be sure to gather all necessary documents and complete the appropriate forms before the filing deadline to avoid penalties.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, the California Franchise Tax Board (FTB) plays a critical role in managing the state's tax system and ensuring compliance among taxpayers. By understanding the FTB's functions and responsibilities, individuals and businesses can better navigate their financial obligations and avoid potential penalties.
We encourage you to take advantage of the resources provided by the FTB to enhance your knowledge of tax laws and improve your financial literacy. If you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from the information. Additionally, feel free to leave a comment or question below, and we'll be happy to assist you further.