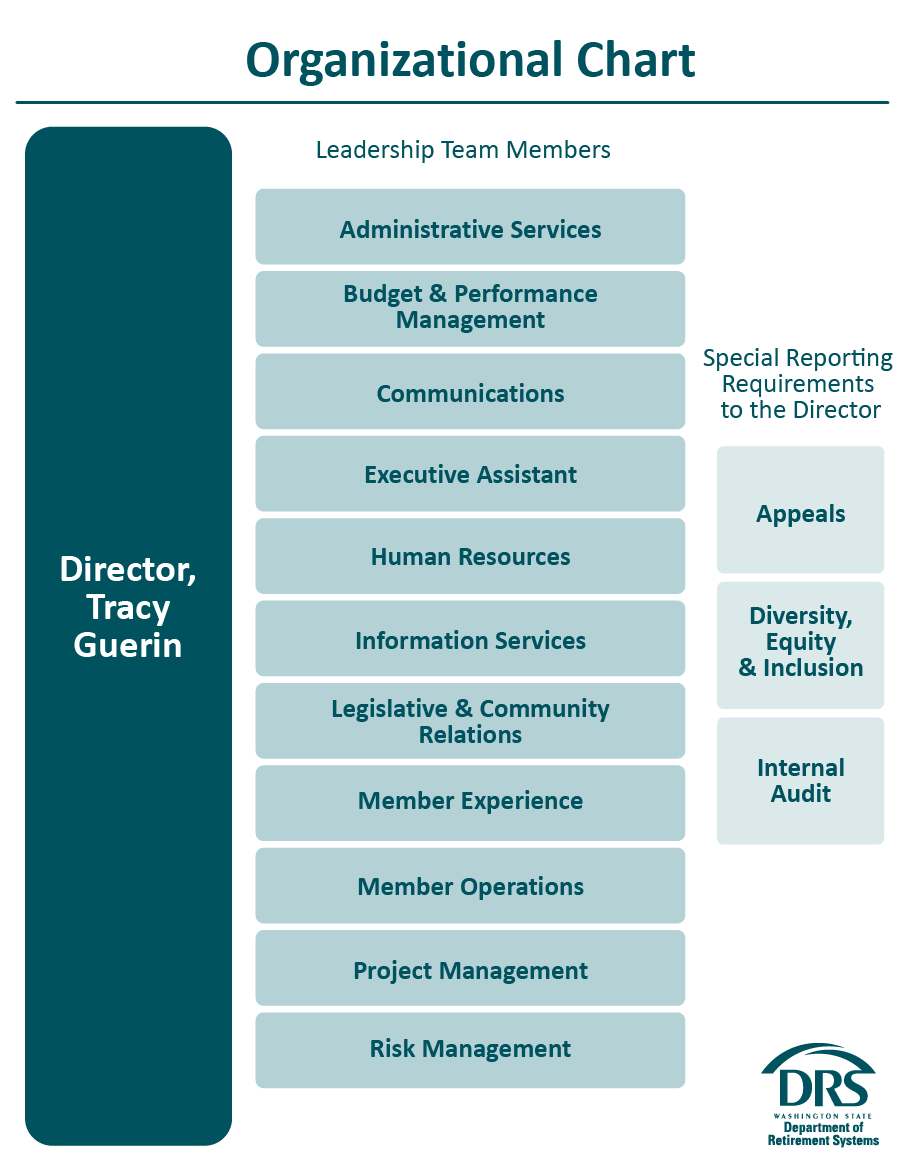
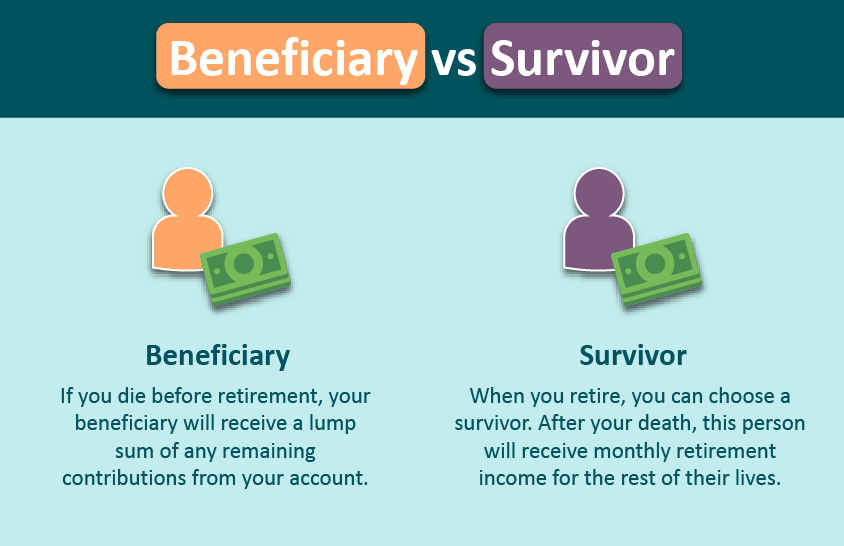
WA DRS has become a crucial element in the world of digital rights management (DRM). It plays a vital role in protecting intellectual property and ensuring that creators receive the compensation they deserve. As digital content continues to grow, understanding WA DRS is more important than ever.
In this era of digital transformation, the demand for secure and efficient digital rights management systems is at an all-time high. WA DRS provides a solution tailored to the needs of content creators, distributors, and consumers alike. By exploring its features, benefits, and implementation strategies, we can gain a deeper understanding of its significance in the industry.
This article will guide you through everything you need to know about WA DRS. From its definition and functionality to real-world applications and challenges, we will cover all aspects of this powerful tool. Let’s dive in and discover how WA DRS can revolutionize the way we manage digital rights.
Read also:Where Is Stefanie Powers Now A Comprehensive Look At Her Current Life And Legacy
Table of Contents
- What is WA DRS?
- How Does WA DRS Work?
- Key Components of WA DRS
- Benefits of Implementing WA DRS
- Challenges in WA DRS Implementation
- Industry Applications of WA DRS
- Future Trends in WA DRS
- Comparison with Other DRM Solutions
- Best Practices for WA DRS
- Conclusion and Call to Action
What is WA DRS?
WA DRS stands for "Digital Rights Management" tailored to specific use cases, often involving content protection in the digital space. It is a system designed to manage and protect digital content from unauthorized use, ensuring that content creators and owners retain control over their intellectual property.
With the rise of digital media consumption, the need for robust DRM solutions has become increasingly apparent. WA DRS addresses this need by providing a secure framework for distributing, managing, and protecting digital assets.
Definition and Scope
At its core, WA DRS is a comprehensive solution that combines encryption, access control, and licensing mechanisms. These features work together to ensure that only authorized users can access and utilize digital content.
- Encryption: Protects content from unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Restricts usage based on predefined rules and permissions.
- Licensing: Manages user access through licenses and subscriptions.
How Does WA DRS Work?
The functionality of WA DRS revolves around several key processes that ensure secure content distribution and management. By leveraging advanced encryption techniques and robust access control mechanisms, WA DRS guarantees that digital content remains protected throughout its lifecycle.
Here’s a breakdown of how WA DRS operates:
Key Processes
- Content Encryption: Digital content is encrypted using industry-standard algorithms to prevent unauthorized access.
- License Management: Licenses are issued to authorized users, granting them access to specific content based on predefined rules.
- Access Control: Users must authenticate themselves before gaining access to the content, ensuring that only legitimate users can consume it.
Key Components of WA DRS
WA DRS consists of several critical components that work together to provide a seamless and secure digital rights management experience. These components include:
Read also:How To Clear Your Icloud Storage A Comprehensive Guide
- Encryption Module: Handles the encryption and decryption of digital content.
- License Server: Manages the issuance and validation of licenses.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Facilitates the efficient distribution of digital content.
Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the security and accessibility of digital content.
Benefits of Implementing WA DRS
Implementing WA DRS offers numerous advantages for businesses and content creators alike. Below are some of the key benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Protects digital content from piracy and unauthorized access.
- Increased Revenue: Enables content creators to monetize their work more effectively through subscription models and pay-per-view options.
- Improved User Experience: Provides users with a secure and convenient way to access digital content.
By leveraging these benefits, organizations can maximize the value of their digital assets while maintaining control over their distribution.
Challenges in WA DRS Implementation
While WA DRS offers many advantages, it also presents certain challenges that must be addressed. Some of the common challenges include:
- Complexity: Implementing WA DRS can be technically challenging, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise.
- Cost: The initial investment in WA DRS infrastructure and software can be significant.
- Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility across different platforms and devices can be a complex task.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, strategic partnerships, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Industry Applications of WA DRS
WA DRS finds applications in various industries, including entertainment, education, and software development. Here are some examples:
Entertainment Industry
In the entertainment industry, WA DRS is used to protect movies, music, and other forms of digital media from piracy. Streaming platforms leverage WA DRS to ensure that only paying customers can access premium content.
Education Sector
WA DRS is also widely used in the education sector to protect e-learning materials and digital textbooks. This ensures that students and educators have access to high-quality content while safeguarding intellectual property rights.
Future Trends in WA DRS
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the landscape of digital rights management. Some of the emerging trends in WA DRS include:
- Blockchain Integration: Leveraging blockchain technology to enhance transparency and security in digital rights management.
- Artificial Intelligence: Using AI to automate license management and detect unauthorized access attempts.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Increasing adoption of cloud-based WA DRS systems for greater scalability and flexibility.
These trends promise to further enhance the capabilities of WA DRS, making it an even more powerful tool for managing digital rights.
Comparison with Other DRM Solutions
While WA DRS offers many advantages, it is important to compare it with other DRM solutions to understand its unique strengths and limitations. Below is a comparison of WA DRS with two popular DRM systems:
WA DRS vs. Adobe DRM
Both WA DRS and Adobe DRM provide robust protection for digital content. However, WA DRS offers greater flexibility in terms of customization and integration with third-party systems.
WA DRS vs. Microsoft PlayReady
Microsoft PlayReady is another popular DRM solution that competes with WA DRS. While both systems offer similar features, WA DRS stands out due to its focus on user-friendly interfaces and ease of implementation.
Best Practices for WA DRS
To maximize the effectiveness of WA DRS, it is essential to follow best practices. Here are some recommendations:
- Regularly Update Software: Ensure that your WA DRS system is always up to date with the latest security patches and features.
- Monitor Usage Patterns: Analyze user behavior to identify potential security threats and optimize system performance.
- Provide User Training: Educate users on the proper use of WA DRS to minimize errors and enhance overall security.
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can ensure that their WA DRS implementation is both secure and efficient.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, WA DRS is a powerful tool for managing digital rights in today’s fast-paced digital landscape. By understanding its functionality, benefits, and challenges, organizations can harness its potential to protect their intellectual property and drive business growth.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with WA DRS in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more insights into digital rights management and related topics.
References:
- World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
- Digital Rights Management Association