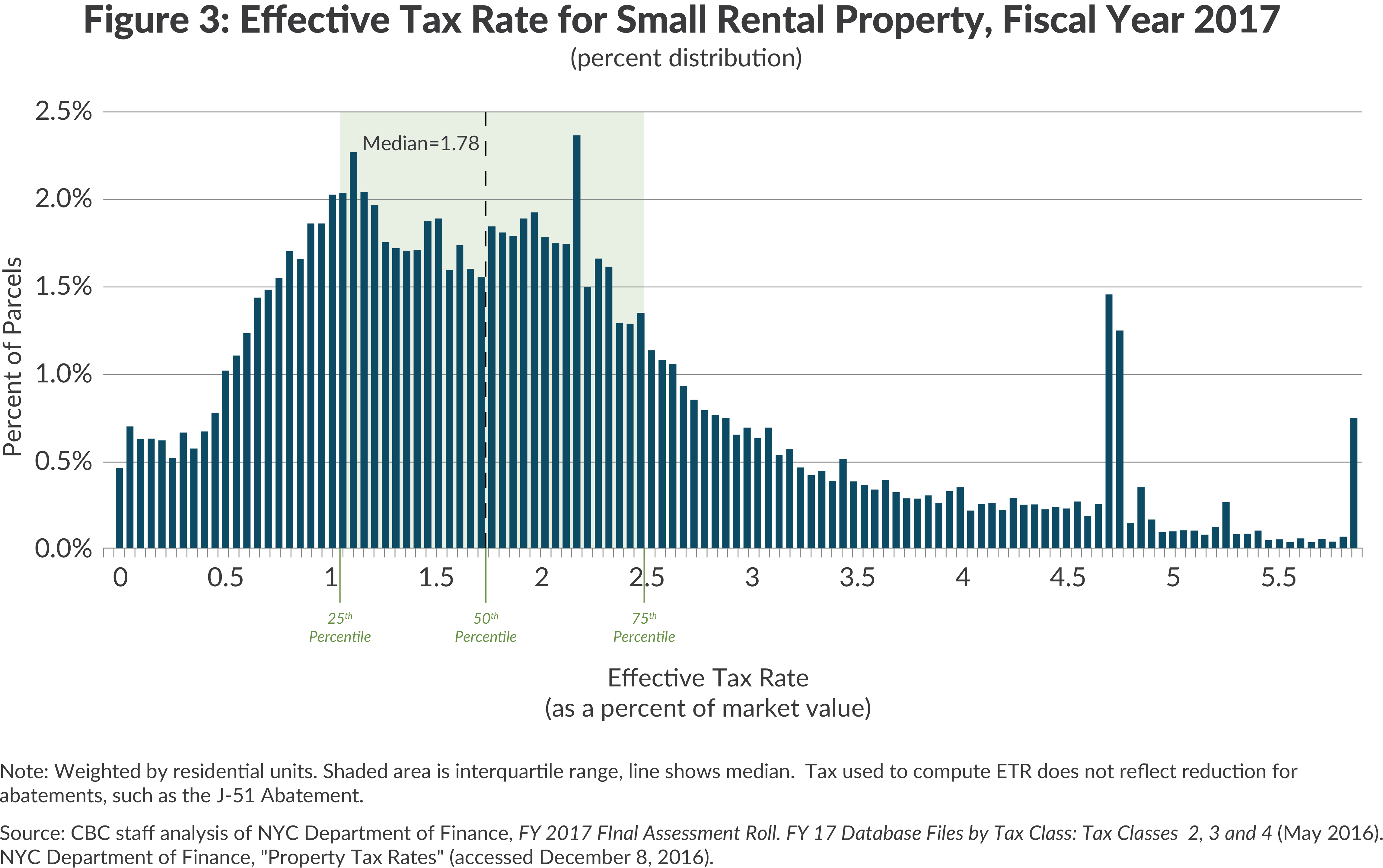
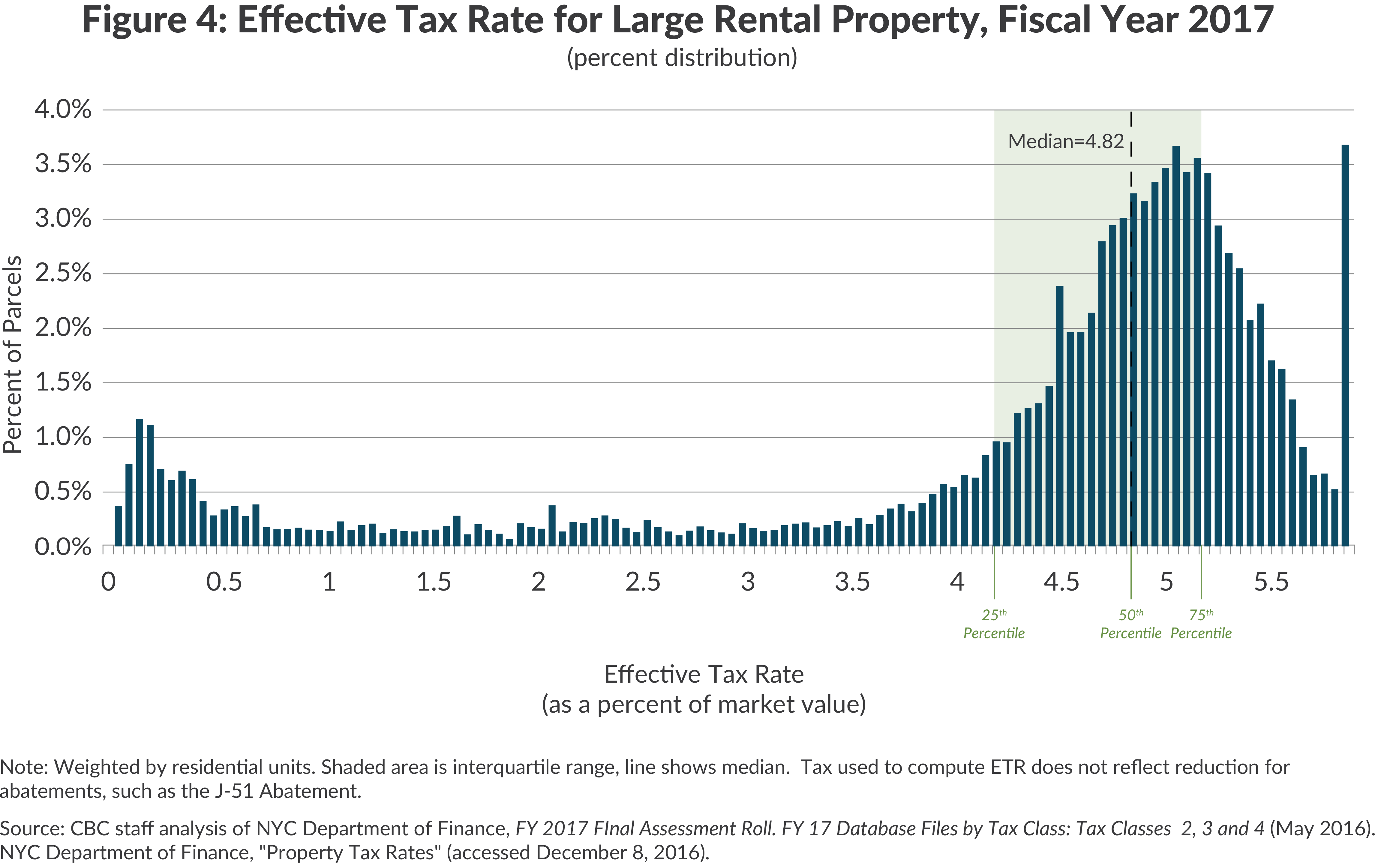
New York City (NYC) state tax is a critical financial obligation for residents, businesses, and visitors alike. Understanding how it works and its implications can save you money and prevent legal issues. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of NYC state tax, covering everything from income tax to sales tax, property tax, and more. Whether you're a resident or planning to relocate, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need.
As one of the most expensive cities in the world, New York City imposes a unique tax structure that combines state and local taxes. This means residents pay not only federal taxes but also state and city taxes. The complexity of NYC state tax often leaves taxpayers confused about what they owe and how to file correctly.
Our goal is to simplify this process by breaking down the components of NYC state tax, offering practical advice, and addressing common questions. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of your tax obligations and how to manage them effectively.
Read also:New York State Taxes A Comprehensive Guide For Residents And Businesses
Table of Contents
- Introduction to NYC State Tax
- NYC Income Tax: Rates and Filing
- Understanding NYC Sales Tax
- NYC Property Tax: What You Need to Know
- Business Taxes in NYC
- Tax Deductions and Credits in NYC
- The Filing Process for NYC Taxes
- Penalties for Late or Incorrect Filing
- Useful Resources for NYC Taxpayers
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to NYC State Tax
New York City is renowned for its vibrant culture, bustling economy, and iconic landmarks. However, it also has one of the most complex tax systems in the United States. NYC state tax encompasses various categories, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, and business tax. Each of these components plays a crucial role in funding public services, infrastructure, and community programs.
For residents, understanding the nuances of NYC state tax is essential for financial planning and compliance. Failure to pay taxes correctly can result in penalties, interest, and legal complications. In this section, we will explore the basics of NYC state tax and its significance in the broader economic context.
Additionally, we will discuss how NYC state tax differs from other states and why it is vital for taxpayers to stay informed about changes in tax laws and regulations.
NYC Income Tax: Rates and Filing
Overview of NYC Income Tax
Income tax is a significant component of NYC state tax. Residents of New York City are subject to both state and city income taxes, in addition to federal taxes. The tax rates vary based on income levels, with higher earners paying a larger percentage of their income.
As of 2023, the New York State income tax rates range from 4% to 10.9% for individuals, depending on their taxable income. Meanwhile, NYC imposes an additional local income tax, with rates ranging from 2.9% to 3.648%. Combined, these taxes can significantly impact a taxpayer's disposable income.
Filing Requirements
- Residents of NYC must file both state and city income tax returns.
- Non-residents who earn income in NYC may also be required to file city income tax.
- Deadlines for filing are typically April 15th, although extensions can be requested.
It is important to note that failure to file on time can result in penalties and interest charges. Taxpayers should consult a tax professional or use tax software to ensure accurate and timely filing.
Read also:Sers Ohio A Comprehensive Guide To Ohios State Employees Retirement System
Understanding NYC Sales Tax
What Is NYC Sales Tax?
Sales tax in New York City is a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and services. The combined state and local sales tax rate in NYC is 8.875%, one of the highest in the country. This tax applies to most tangible personal property and certain services, with some exceptions for essential items like groceries and clothing under $110.
How It Affects Consumers
Consumers in NYC must factor sales tax into their purchasing decisions. For example, buying a $100 item in NYC would cost $108.88 after tax. Businesses are responsible for collecting sales tax from customers and remitting it to the state and city authorities.
Exemptions and Special Cases
- Certain items, such as prescription medications and groceries, are exempt from sales tax.
- Some businesses may qualify for sales tax exemptions if they purchase goods for resale or business use.
- Tourists and out-of-state visitors are subject to the same sales tax rates as residents.
Understanding these exemptions can help consumers and businesses save money and comply with tax laws.
NYC Property Tax: What You Need to Know
Overview of Property Tax in NYC
Property tax is another critical component of NYC state tax. It is assessed on real estate properties, including residential homes, commercial buildings, and vacant land. Property taxes in NYC are calculated based on assessed value, which is determined by the city's Department of Finance.
How Property Tax Works
Property owners in NYC receive an annual tax bill based on their property's assessed value. The tax rate varies depending on the property class, with residential properties generally having lower rates than commercial properties. As of 2023, the average property tax rate in NYC is around 1.17% for homes and 2.37% for commercial properties.
Appealing Property Tax Assessments
- Property owners who believe their assessment is incorrect can file an appeal with the New York City Tax Commission.
- The appeal process involves submitting evidence to support a lower valuation.
- Timely filing is essential to ensure consideration of the appeal.
Understanding the property tax system and your rights as a property owner can help you avoid overpayment and reduce your tax burden.
Business Taxes in NYC
Types of Business Taxes in NYC
Businesses operating in New York City are subject to various taxes, including corporate income tax, payroll tax, and business registration fees. The corporate income tax rate in NYC is 8.85%, in addition to state and federal taxes. Small businesses may qualify for reduced rates or exemptions.
Payroll Tax Responsibilities
Employers in NYC must withhold income taxes from employee wages and remit them to the appropriate authorities. They are also required to pay unemployment insurance taxes and contribute to the New York State Workers' Compensation Board.
Compliance and Record Keeping
- Businesses must maintain accurate records of all financial transactions.
- Annual tax filings are mandatory for all businesses, regardless of size.
- Failure to comply with tax regulations can result in fines, penalties, and legal action.
Consulting a tax advisor or accountant can help businesses navigate the complexities of NYC business taxes and ensure compliance.
Tax Deductions and Credits in NYC
Common Tax Deductions
Taxpayers in NYC can take advantage of various deductions to reduce their taxable income. Common deductions include mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and business expenses. Additionally, homeowners may qualify for property tax deductions if they itemize their deductions on their federal tax return.
Available Tax Credits
NYC offers several tax credits to help taxpayers reduce their overall tax liability. Some of these credits include:
- Child Tax Credit
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
- Senior Citizen Rent Increase Exemption (SCRIE)
- Cooperative and Condominium Credit
Taxpayers should consult the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance for a complete list of available deductions and credits.
The Filing Process for NYC Taxes
Steps to File NYC Taxes
Filing NYC taxes involves several steps, including gathering necessary documents, calculating tax liability, and submitting the appropriate forms. Taxpayers can file electronically through the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance website or use certified tax preparation software.
Gathering Required Documents
- W-2 forms from employers
- 1099 forms for freelance or contract work
- Property tax bills and mortgage statements
- Receipts for deductible expenses
Having all documents organized and ready can streamline the filing process and reduce the risk of errors.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Forgetting to include all sources of income
- Miscalculating deductions or credits
- Missing deadlines or filing extensions
Seeking professional assistance can help taxpayers avoid these common pitfalls and ensure accurate filings.
Penalties for Late or Incorrect Filing
Consequences of Late Filing
Failure to file NYC taxes on time can result in significant penalties and interest charges. The late filing penalty is generally 5% of the unpaid tax for each month or part of a month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. Additionally, interest is charged on the unpaid tax at the rate of 8% per year.
Correcting Errors in Tax Returns
If a taxpayer discovers an error in their filed return, they can submit an amended return using Form IT-255. Amended returns must include all necessary documentation and corrections. The IRS and state authorities will review the amended return and make adjustments accordingly.
Seeking Professional Help
Taxpayers who are unsure about their filing obligations or have made mistakes in previous filings should consult a tax professional. They can provide guidance on resolving issues and avoiding future penalties.
Useful Resources for NYC Taxpayers
There are several resources available to help NYC taxpayers understand and manage their tax obligations. These include:
- New York State Department of Taxation and Finance
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
- Local tax preparation services
- Online tax software platforms
Additionally, many community organizations offer free or low-cost tax assistance programs, particularly for low-income individuals and seniors.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, NYC state tax is a multifaceted system that requires careful attention and planning. By understanding the various components of income tax, sales tax, property tax, and business tax, taxpayers can better manage their financial responsibilities and avoid potential pitfalls. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of NYC state tax, including rates, filing requirements, deductions, and resources.
We encourage readers to take action by reviewing their tax obligations, gathering necessary documents, and seeking professional advice if needed. Additionally, sharing this article with others can help spread awareness about NYC state tax and promote financial literacy. For more information on related topics, explore our other articles and resources.